Audio Version: Press Play to Listen
From detecting lung cancer and COPD to triaging pulmonary embolism cases, this article explores the expanding role of AI in chest imaging.
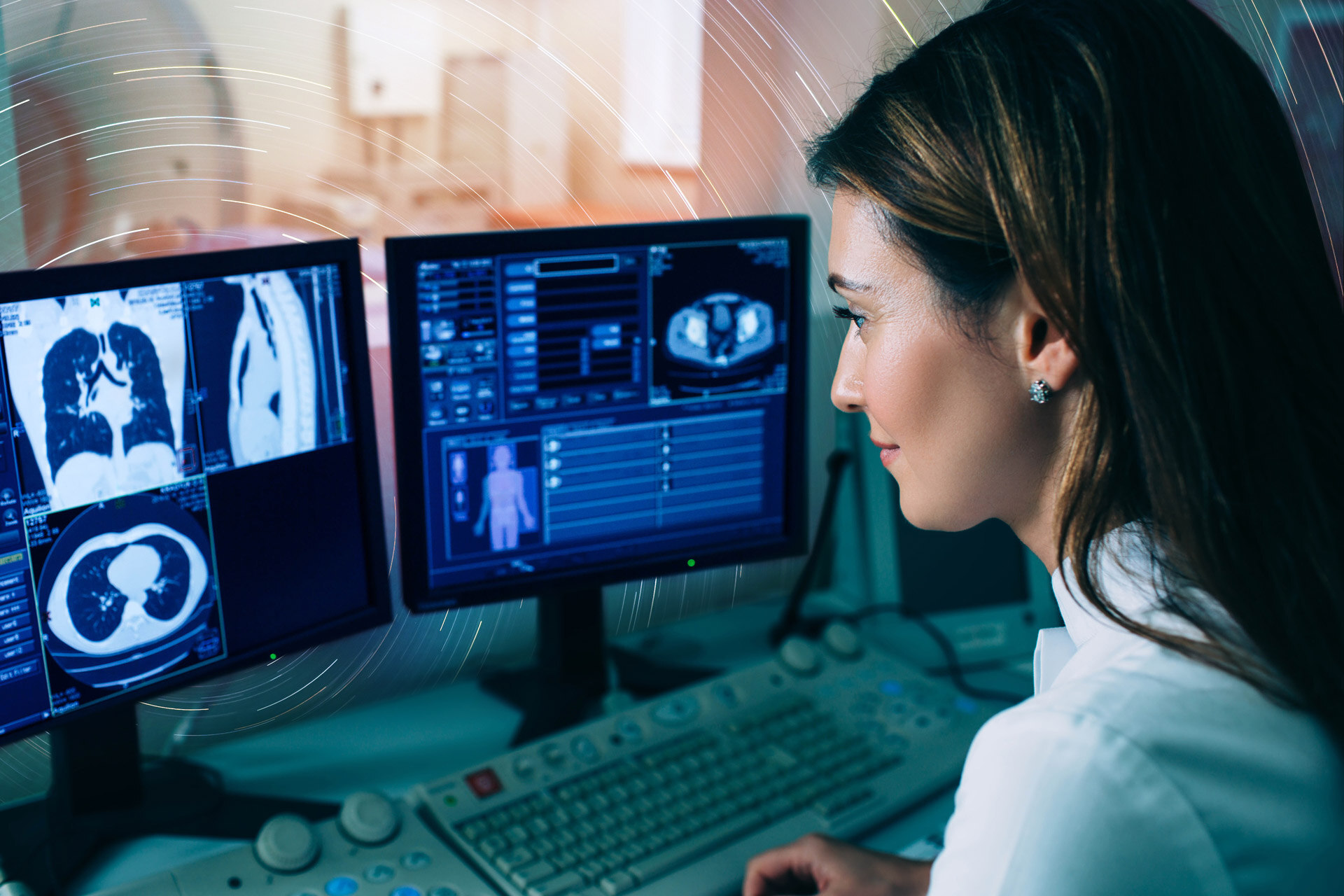
Medical imaging has long been a cornerstone in evaluating the lungs, both anatomically and functionally. Early and accurate imaging is crucial for diagnosing conditions like lung cancer, COPD, and interstitial lung diseases (ILDs). Whether it's for establishing a diagnosis, monitoring disease progression or screening, chest imaging serves multiple purposes and employs techniques such as X-rays and CT scans.
However, radiology departments face increasing pressure due to growing workloads and staffing shortages, and AI tools are emerging as a solution to these challenges in pulmonary diagnostic imaging.
By assisting with abnormality detection, improving diagnostic accuracy, streamlining reporting, and even aiding prognosis in pulmonary conditions, AI is helping radiologists meet escalating demands. These advances ultimately enable earlier interventions and improved patient outcomes.
We explored some of the key areas and how AI can be used to help transform pulmonology.
AI in the Emergency Room
In diagnostic imaging, delayed or missed findings pose serious challenges, particularly with acute, life-threatening conditions. AI is playing an increasingly vital role in identifying and prioritizing critical medical conditions as quickly as possible.
Take pulmonary embolism, for instance – a major global health concern, responsible for many deaths, illnesses, and hospital stays worldwide. AI solutions can now swiftly and automatically detect pulmonary embolism cases from chest CT scans. In addition, AI can identify potential pulmonary embolisms in patients undergoing scans for other health issues, such as suspected oncological conditions.
Another life-threatening condition, aortic dissection, though rare, requires prompt detection for better outcomes. AI tools can quickly identify acute aortic dissections needing immediate attention and provide real-time alerts during thoraco-abdominal angiography. This ensures that patients receive timely treatment, significantly improving their chances of recovery.
AI is also aiding in diagnosing dilated cardiomyopathy, a potentially fatal heart disease that enlarges the ventricles. AI tools automatically process CT scans to measure ventricular dilation, reporting the RV/LV ratio and supporting physicians to diagnose this condition.
AI for Chest X-rays
Despite advancements in medical imaging, chest X-rays remain one of the most commonly performed diagnostic procedures worldwide. They capture essential health data, including images of the heart, lungs, airways, blood vessels, and bones. In many countries, chest X-rays are the first line of imaging for assessing pulmonary and cardiac conditions. The increasing demand for quick and accurate interpretation places significant pressure on radiologists.
However, interpreting chest X-rays can be complex, influenced by factors like patient positioning and image quality. Subtle abnormalities, shadowing, and tissue superimposition can lead to misdiagnosis. Radiologists often rely on what their eyes can detect, but AI can provide additional support in the fast and accurate detection of cardio-thoracic diseases, leading to better patient outcomes.
Recent AI developments allow for the detection of over 100 different findings on chest X-rays in seconds, improving both radiologist accuracy and productivity. Using advanced deep learning technology, AI can identify abnormalities like pleural effusions, pneumothorax, and consolidation, providing visually verifiable analyses. Some tools can even detect incidental findings such as early-stage cancer indicators like nodules.
AI can also help prioritize exams based on urgency, streamlining workflow in radiology departments. By identifying cases without abnormalities, AI can help free up radiologists to focus on cases that require further investigation and pave the way towards autonomous reporting.
AI for Chest CT and Lung Cancer Screening
Chest CT scans offer improved anatomical delineation compared to X-rays and have become a cornerstone in modern medical imaging. However, evaluating chest CTs can be complex and time-consuming. AI tools can help radiologists read chest CT images more efficiently, improving workflow and diagnostic quality.
AI provides both qualitative and quantitative insights, enabling radiologists to objectively assess cardio-thoracic diseases over time, directly from their native viewer. Automating routine tasks with AI allows radiologists to concentrate on more complex cases and patient interactions.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States, and early detection is crucial. Low-dose chest CT scans are widely used in lung cancer screening programs globally, but analyzing these scans for pulmonary nodules can be tedious and error-prone. Advances in AI now allow for the automated detection, classification, and growth assessment of lung nodules, speeding up diagnosis and enabling radiologists to interpret scans more efficiently.
Beyond lung cancer, AI tools can identify other conditions such as emphysema and coronary artery calcification, providing a more comprehensive assessment of cardio-thoracic health.
AI is increasingly being used to automate key aspects of lung density assessment which can be used to help assess conditions such as emphysema and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Some tools even offer 3D visualization and lung segmentation techniques for quantification of high- and low-attenuation areas and compare current images with prior scans to flag disease progression over time.
AI for Reporting
Many AI applications also contribute to one of the most vital aspects of a radiologist’s work: reporting.
AI systems can generate structured reports that offer both quantitative data and visual aids, assisting in diagnosis and treatment planning. For example, chest X-ray tools can create complete, editable draft reports, streamlining the radiology workflow.
AI can also analyze lung cancer screening results and generate reports, automating time-consuming tasks and enhancing efficiency.
Finally, AI can also help ensure that follow-up recommendations made in radiology reports are acted upon.
Choosing the right Pulmonology AI application
The integration of AI offers healthcare providers a clear opportunity to boost efficiency and streamline operations. However, as this article has demonstrated, healthcare providers face a wide array of choices, and one significant challenge is identifying the AI solution that best suits their unique requirements. Addressing this and other challenges can be effectively achieved by partnering with a single strategic AI platform provider, such as Blackford, which enables organizations to evaluate and validate AI solutions with their own data prior to making purchasing decisions.
The rapid growth of AI tools in pulmonology, as well as in other medical fields, has led to the development of many algorithms that may appear quite similar. Blackford understands the challenges providers encounter when making these decisions – what works perfectly for one healthcare institution might not work well for another, due to factors like patient population, scanner type, or other unique variables. By offering multiple applications that address the same clinical use cases, the Blackford platform allows healthcare organizations to determine which solution is the most effective for their institution’s unique needs.
Why a Platform approach to AI makes sense
Centralizing access to AI solutions via a dedicated platform empowers healthcare providers to more efficiently evaluate, implement, and manage a broad range of imaging AI applications. This not only helps to maximize the utilization of resources but also reduces deployment timelines and financial burdens. Furthermore, it simplifies training, monitoring, and support efforts by consolidating these processes into a unified system.
A platform-centric approach offers additional benefits by streamlining various operational aspects, such as contract management, deployment procedures, and ongoing support. Importantly, AI platforms integrate seamlessly with existing hospital systems, ensuring optimal performance, especially when handling DICOM interfaces.
Moreover, such platforms offer access to a portfolio of pre-vetted AI applications that span multiple medical and operational areas beyond pulmonology, including cardiology, neurology, MSK, trauma, and breast imaging. Hospitals can acquire comprehensive and complementary bundles of AI applications through a single contract, thus eliminating the complexities involved in purchasing individual algorithms.
Ultimately, by adopting a single-platform strategy, clinicians and institutions gain access to a diverse range of AI solutions, facilitating the rapid adoption of new technologies and ensuring the deployment of applications tailored to their specific needs.
Interested in learning more about the Pulmonology AI applications available on the Blackford Platform?